Medical Devices
Brief Review of Post-Market
Surveillance Activities

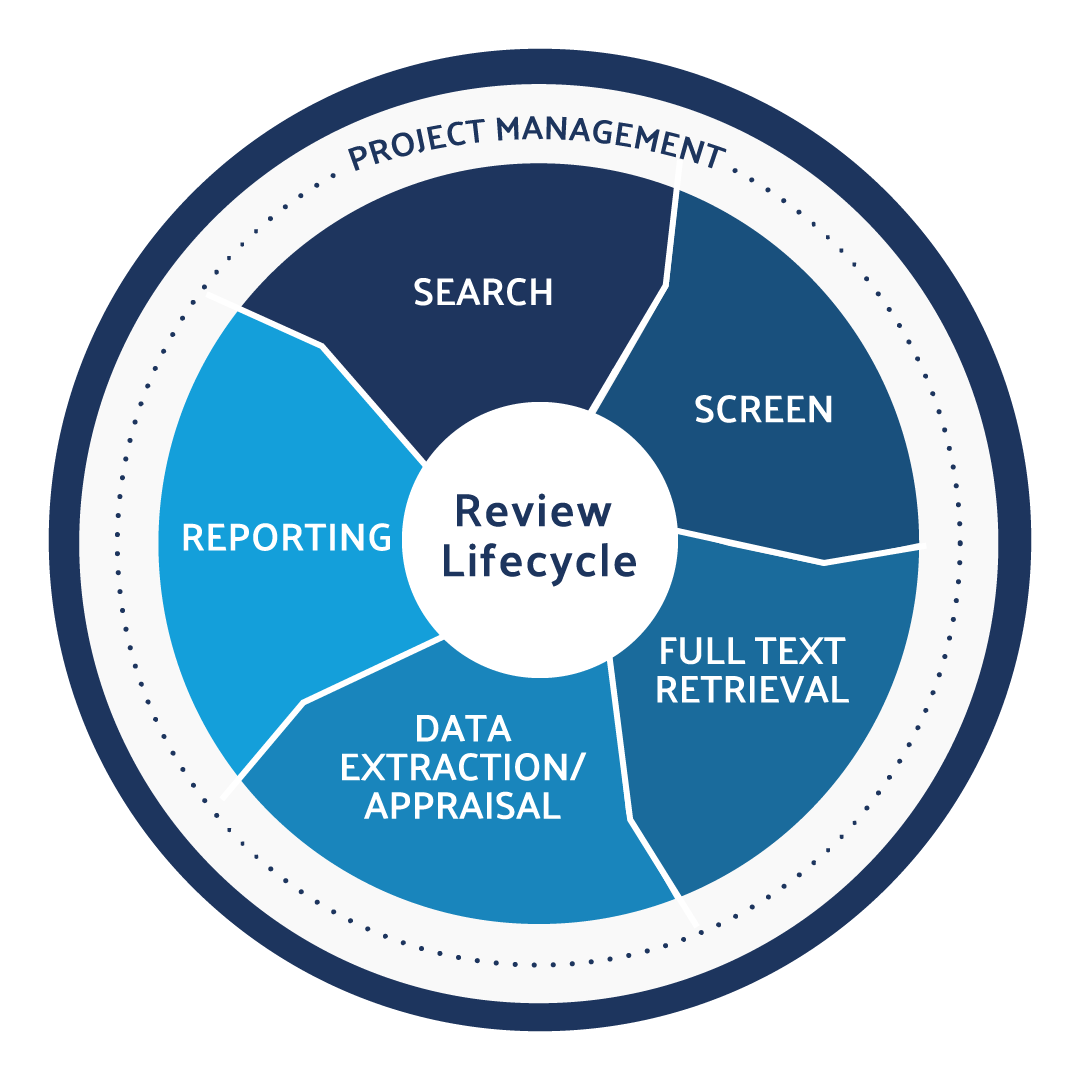
Use DistillerSR to produce CER and PER literature reviews in an efficient, audit-ready, and compliant way.
Post-market surveillance (PMS) is a systematic procedure to proactively collect and evaluate experience gained from available devices. This surveillance is crucial because certain risks may only surface after use or during transport, storage, or cleaning.
PMS typically focuses on reactive data collection, in which manufacturers gather and report adverse events from a device after it’s been released. These events are reported to manufacturers or regulatory bodies like the FDA in the U.S., MHRA in the U.K., and Health Canada in Canada. The requirements are slightly different across regulatory bodies, and many offer post-market surveillance medical device guidance.
In this article, we will delve into the specifics of PMS, why it is important, and how to set up a successful PMS system.
What Is PMS?
Post-market surveillance refers to monitoring and tracking the safety and performance of medical devices, in-vitro diagnostics, pharmaceuticals, and other products after they have been approved for sale and use by regulatory authorities. This includes monitoring for serious incidents or adverse events, tracking product performance and usage, and collecting data to identify issues that may arise in the real-world use of the product.
The goal of post-market surveillance is to ensure that products continue to be safe and effective for patients and consumers, to ensure that the product continues to perform as intended against claims made about the product, and to identify any problems that may arise before they cause significant harm.
What Are PMS Activities?
PMS activities are a set of activities administered by manufacturers. They include gathering and analyzing data on medical devices that are available on the market, then determining if any action needs to be taken.
These steps are essential in ensuring that devices remain safe and effective and that necessary measures are taken if the risk of using the medical device exceeds the benefit. Evaluating post-market surveillance results can also identify areas of continuous improvement for medical devices. Some examples of post-market surveillance activities include:
1. Adverse Event Reporting
Manufacturers and distributors must report any negative events or incidents associated with using a medical device to the FDA (or relevant notified body). This includes deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions likely cause or contribute to death or serious injury.
2. Risk Management
Risk management in PMS involves identifying and assessing potential risks associated with using a medical device and taking steps to mitigate or eliminate those risks. This can include monitoring adverse event reports, conducting testing on returned product or performance evaluation studies, and making changes to the device’s design or labeling.
3. Evaluation Of Clinical And Performance Data
Clinical evaluation in PMS is the process of assessing a medical device’s clinical performance and safety through the analysis of data from various sources such as clinical studies, registries, and adverse event reports.
4. Compliance With FDA Regulations
Manufacturers and distributors must comply with post-market surveillance requirements and failure to do so can result in penalties, such as fines or removal of a device from the market. The FDA conducts quality audits and on-site inspections to ensure that manufacturers and distributors follow the regulations, including adequate PMS processes for handling of complaints.
5. Product Performance Monitoring
Manufacturers and distributors must collect data on the performance of a medical device over time, such as product performance data, device utilization data, and customer feedback. This data is regularly reported to the FDA.
6. Product Testing
Manufacturers and distributors should conduct testing to ensure a medical device meets the safety and effectiveness standards set by the FDA and that the device’s performance does not change over time. If you’ve ever wondered what a periodic safety update is, it comes from this kind of data.
Learn More About DistillerSR
(Article continues below)
Why Are Post-Market Surveillance Activities Crucial?
Post-market surveillance aims to differentiate between defective devices on the market and those that are safe and effective. With more evidence, unsafe devices are less likely to remain on the market, thereby improving the quality of treatment.