About Systematic Reviews
A Peer Review vs a Systematic Review

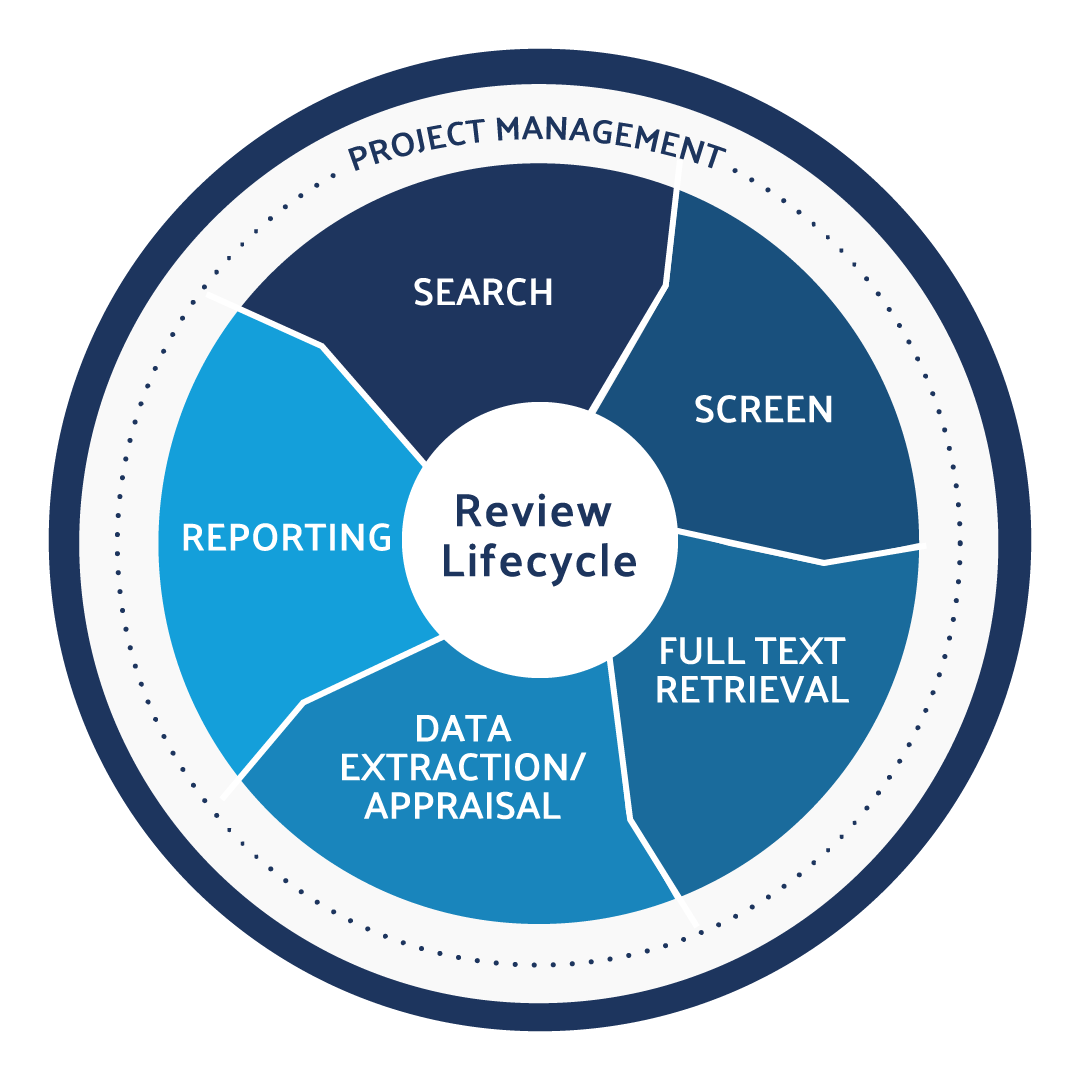
Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
In this article, we will look at what a systematic review is, and how it is different from a peer review.
What Is A Systematic Review?
A systematic review uses explicit methods to identify, select, and critically appraise relevant primary research. It attempts to review all the available evidence to answer a clearly formulated research question. Systematic reviews use inclusion or eligibility criteria to filter out studies irrelevant to the search topic. They are hallmarks of the evidence synthesis process in scientific research since they use all eligible existing research on a topic. Unlike research papers like RCTs that report primary data, systematic reviews report on the findings by combing primary information extracted from eligible studies. This makes systematic reviews a secondary report of data. The methodology involved is rigorous, transparent, and reproducible, this makes systematic reviews a high-quality source of information.
The Systematic review methodology involves the following steps.
- Formulating and stating a clear research question to answer (PICO approach)
- Developing a protocol (with strict inclusion and exclusion criteria for the selection of primary studies)
- Performing a detailed and broad literature search
- Critical appraisal of the selected studies
- Data extraction from the primary studies included in the review
- Data synthesis and analysis using qualitative or quantitative methods [1].
Following this methodology, systematic reviews produce high-quality and reliable evidence to guide clinical practice and inform policy development.
Learn More About DistillerSR
(Article continues below)
What Is A Peer Review?
Peer review is a system to assess the quality of a manuscript submitted by the author before it is published. Independent researchers in the same discipline assess the manuscripts for originality, quality, validity, and significance to help editors determine if they can be published in their journal. Based on the quality score awarded by the reviewers, the manuscript may be forwarded to a more fitting journal. For example, high-quality manuscripts are forwarded to high-quality journals, this leads to categories called journal classes. These independent reviewers may or may not have competencies similar to the authors of the manuscript.
How Does A Peer Review Work?
When a manuscript or an article is submitted to a journal, it is assessed by the editor to see if it meets the criteria for submission. Once it is confirmed that it satisfies the criteria, the editorial team then selects potential peer reviewers within the same field to evaluate the manuscript.
Single-blind, double-blind, or open reviewing, are techniques used to assess the originality, quality, validity, and significance of the manuscript. A variation from these standard approaches is the transparent, collaborative, and post-publication peer reviews.
Different journals use any of these methods to evaluate the quality of the content they publish. You can find out which peer-review system is used by a particular journal on their “about” page.
Why Do We Need A Peer Review?
Peer reviews are designed to assess the validity, quality, and originality of scientific articles that are published. This helps in maintaining the integrity of scientific literature by filtering out poor articles. Peer reviewers are experts in a certain field who volunteer their time to help improve the quality of manuscripts that are published. They help point out gaps in articles that may require further explanation and suggest changes to make a paper easier to read, and more useful in the field.
Conclusion
Researchers mustn’t confuse these two types of reviews. A systematic review involves reviewing all the available eligible literature to find credible, and reliable evidence to answer a specific research question. A peer review, on the other hand, is done by other authors in the same discipline and evaluates the quality, validity, and originality of a single article before it is published. The process of peer review establishes confidence in the articles that are published in a journal. Systematic reviews then search for and collect studies that have been peer-reviewed, to synthesize evidence found in them. Systematic reviews, after their completion by the author, are also peer-reviewed before publication.
References
Linares-Espinós E, Hernández V, Domínguez-Escrig JL, Fernández-Pello S, Hevia V, Mayor J, et al. Metodología de una revisión sistemática. Actas Urol Esp. 2018;42:499–506.